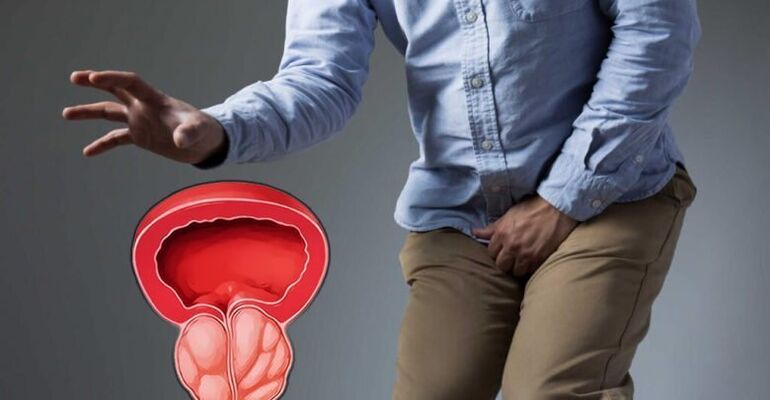
Causes of chronic prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is caused by inadequate or short-term treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis.
symptom
- Discomfort or pain - perineum, lower abdomen, groin, scrotum, penis, during ejaculation
- Urinary changes - difficulty urinating, frequent urination, small urine output, feeling of incomplete bladder emptying.
Many leading urologists believe that erectile dysfunction in patients with chronic prostatitis is caused by psychogenic and neurological problems.
diagnosis
Submission of semen for bacteriological examination is included in the diagnostic algorithm for male genital infections and investigation of male infertility.
In many men over the age of 30, ultrasound may show diffuse changes in the prostate. However, fibrotic processes do not indicate the presence of prostatitis.
According to routine examination results, there is no specific case of chronic prostatitis.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis
- Pelvic floor muscle training – There is some evidence that specific exercises are effective in reducing symptoms of chronic prostatitis and chronic pelvic pain syndrome;
- Acupuncture – A few studies have shown benefits of acupuncture compared with placebo in people with chronic prostatitis;
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy - based on the effect of acoustic pulses of significant amplitude on connective and bone tissue, widely used to treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system and more recently in urology, where its effectiveness is under investigation;
- Behavioral therapy and psychological support - Since chronic prostatitis is associated with poor quality of life and the development of depression, these approaches can improve the patient's psychological state and help reduce some symptoms of the disease.